TL;DR
➡ Naturally, 50-100 hair follicles in your scalp die daily and are replaced with new ones. But if your hair is falling out faster than you reproduce, then there is balding.
➡ The most common reasons for hair loss are genetic background, aging and side effects of certain medications.
➡ You can stop your hair loss by first identifying and eliminating these reasons. After consulting your doctor, you can start changing your lifestyle and using hair regrowth medications such as Finasteride or Minoxidil.
We all love our hair.
It’s the very thing that completes our appearance.
Whatever your go-to hairstyle is, if your hair looks good, you feel good; there’s no arguing that.

Seeing a few strands of hair fall out when you’re combing is likely to shake your mood. But once we see a tangible sign of hair loss like our hairline receding or our hair thinning, that’s the real mood killer.
The first step to stopping and reversing hair loss is, just as it is with any other medical condition, is to understand the reason behind it.
So in this article, I will explain every known reason behind hair loss, including COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2), and help you identify the cause of your hair thinning.
Table of Contents
Science Behind Hair Loss, Simplified
Hair is made of keratin, a structural protein found in your skin and nails.
Produced in the hair follicles right at the outside layers of your skin, a hair strand is a product of hair follicles’ lifecycle.
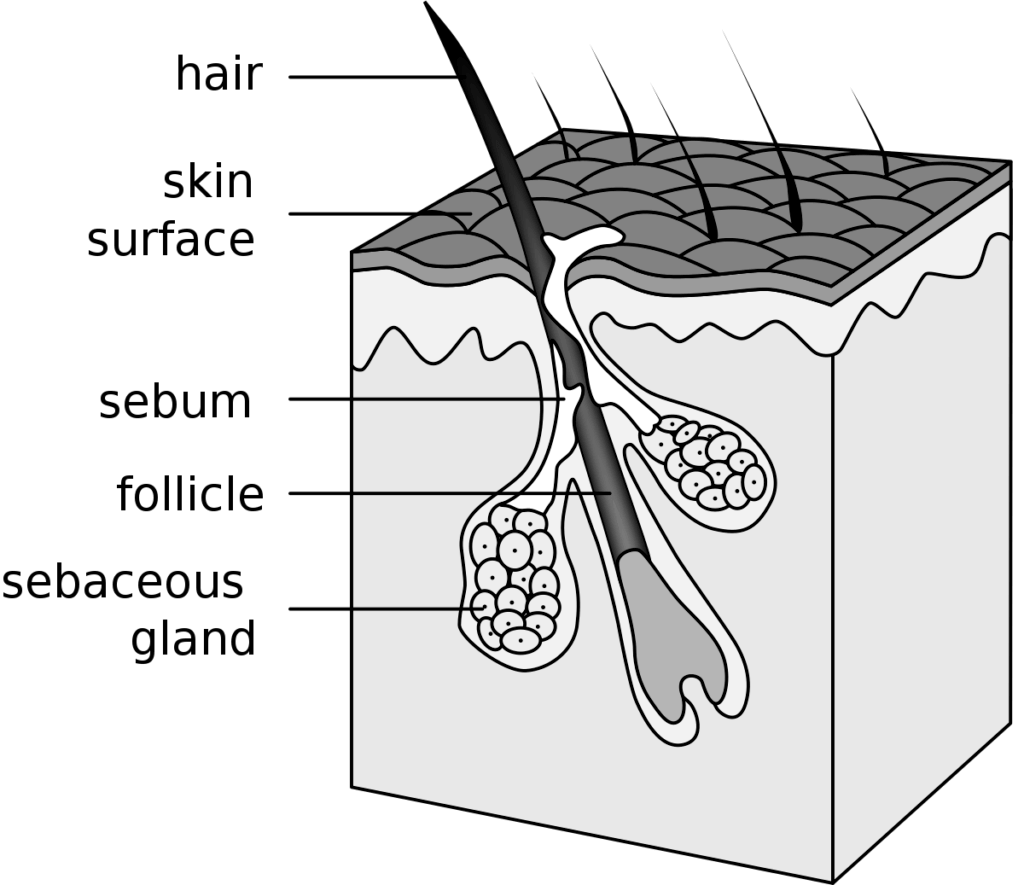
A hair follicle is produced, then it grows for a while, then it slowly dies, and new hair replaces it.
So around 50-100 hair follicles in your scalp die every day and are replaced with new ones. That much loss is unnoticeable since the average person has 100,000 hairs on the head.
When a hair follicle on your head dies, it falls out, which is what you see when you comb through your hair. Your hair falling out is the most natural thing in the world, and as long as the new hair grows to replace the lost ones, you’re OK.
You only go bald if one of these two situations are present:
1️⃣ You’re losing more hair than you can reproduce
2️⃣ You’re reproducing less hair than you lose
I know these two sound like the same thing, but they’re not.
You can either be losing hair fast or producing new hair slowly, which both result in a number of hair follicles permanently reduced.
And all the reasons behind hair loss cause either of these two situations. Identifying what it is is up to you or your dermatologist.
Now let’s see all the reasons that might be causing the gap between dead and born hair follicles:
24 Causes for Hair Loss
Here are 25 of the most common reasons behind hair loss and baldness:
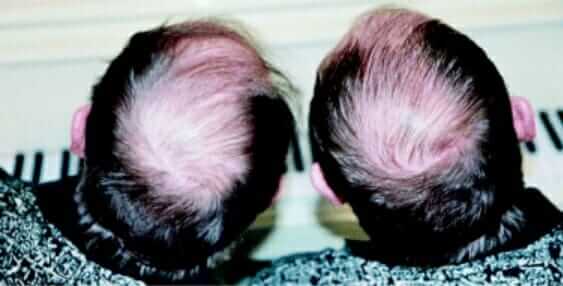
1- Genetic Background
You are way more likely to experience hair loss if you have a family history of hair loss, either on the maternal or paternal side.
You are way more likely to experience hair loss if you have a family history of hair loss, either on the maternal or paternal side.
The most widespread cause of hair loss is genetic female and male pattern hair loss. A common idea suggests that if your paternal grandfather is bald, you’re going bald, and if not, you’re safe.
Although this can be considered a variable in hereditary hair loss, there’s more to a genetic background in terms of hair loss, much more. Over many years and across different studies, researchers have found that over 280 genes play a role in hair loss. Still, you don’t need to look at each one to know if genetics causes hair loss for you.
In short, the history of hair loss among relatives from maternal and paternal sides should be asked to know if your hair loss comes from a genetic background. If there’s a pattern in the family history, hair loss can be related to your genetics.
“If you look at identical twins — who share 100 percent of their genes — typically, they have a very similar pattern of hair loss.”
Markus Nöthen, a geneticist at the University of Bonn
2- Age
Overall cell production, and production of any kind, slow down with age.
And hair growth is not an exception.
Especially after your 40s, you’re likely to experience a receding hairline and overall thinning in your hair. These might not come in a pattern, but it is expected to worsen if you have a genetic background for balding.
3- Androgen Sensitivity
This one requires a bit of explanation, so bear with me:
Androgens are a group of hormones present in both men and women and play a role in male traits and reproductive activity, such as testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Around puberty, androgens stimulate axillary and pubic hair in both sexes. However, later, high amounts of androgens cause hair loss.
In simplest terms, high levels of androgens, especially DHT, cause your androgen-sensitive hair follicles to shrink and shorten the hair growth cycle. These levels end up with you having thinner hairs that fall out faster.
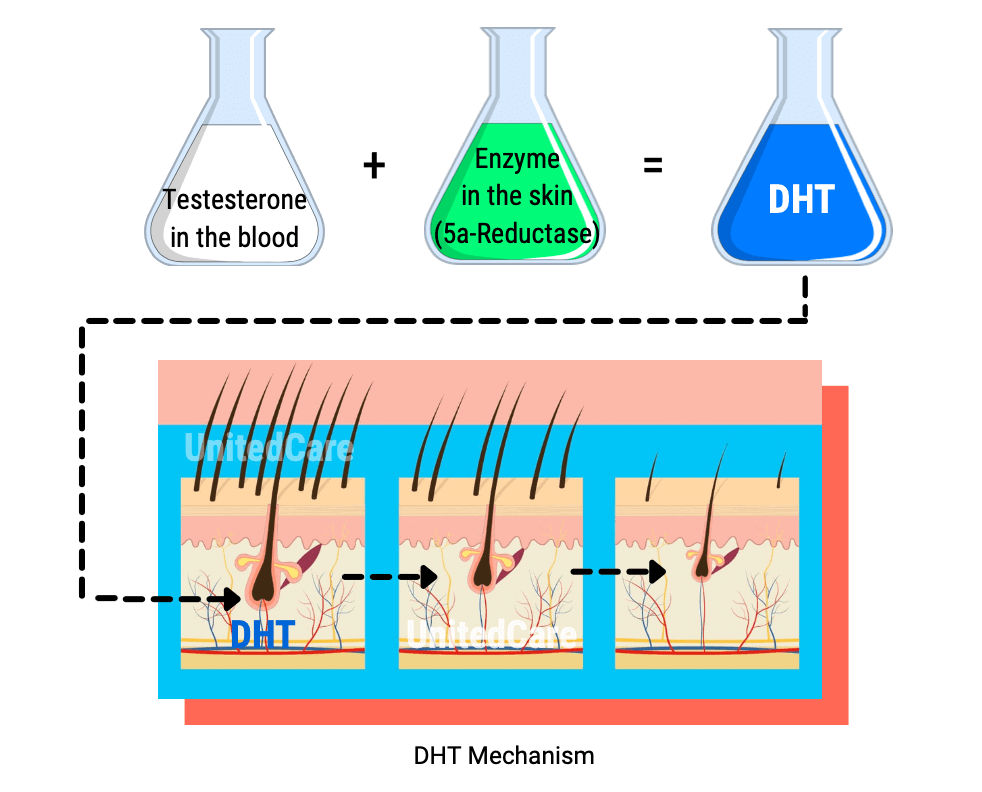
In addition to the number of androgens, follicular androgen sensitivity, determined by genetics, plays a huge role in hair loss.
Generally, hair follicles on the side and back of the head are inherently more DHT resistant since they have fewer ARs (Androgen Receptors). When transplanted to a recipient area, they keep their DHT resistance, making the hair transplant surgery results permanent.
While research shows that a high level of DHT and Androgen Sensitivity cause male pattern baldness (AGA), only about a third of women with AGA show abnormally high androgen levels
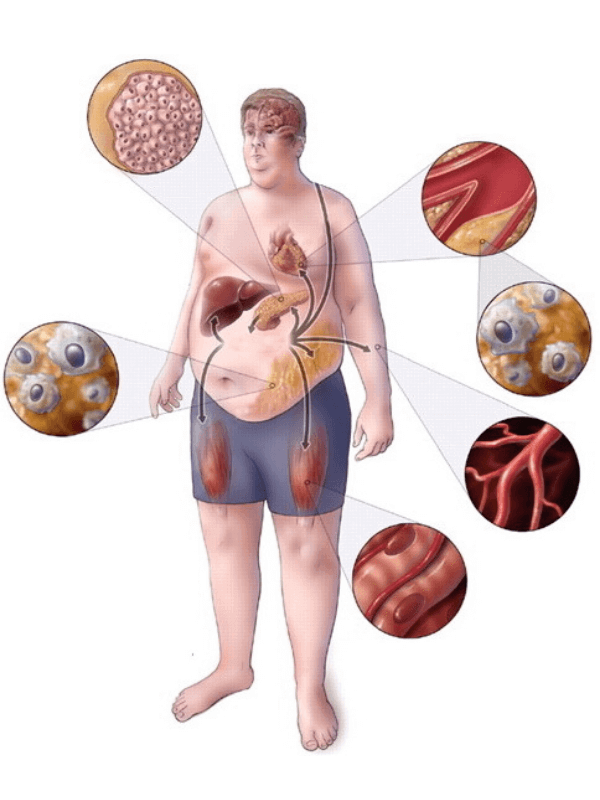
4- Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) refers to metabolic abnormalities that include hypertension, central obesity, and atherogenic dyslipidemia.
It is strongly associated with the risk of developing diabetes and heart diseases. On the other hand, insulin resistance refers to high plasma insulin levels in the blood. It can also be considered an abnormality in MetS.
Those with metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance are more likely to experience hair loss than those without because the three conditions are linked., as studies suggest.
According to the NCEP ATP III definition, metabolic syndrome is present if three or more of the following five criteria are met:
▶ A waist larger than 101cm (40 inches) for men or 89cm (35 inches) for women
▶ Fasting blood sugar over 100 mg/dl
▶ Fasting triglycerides over 150 mg/dl
▶ Blood pressure over 130/85 mmHg
▶ Fasting HDL cholesterol less than 40 mg/dl for men or 50 mg/dl for women
5- Medications
Medications interfere with the normal hair growth cycle, causing permanent or temporary hair loss.
The most common medications that cause hair loss, or androgenic alopecia, are anticoagulants (blood thinners such as warfarin), cancer chemotherapy agents, and organ transplant immunosuppressant drugs.
Other medications that can cause a form of hair loss include:
- Antidepressants
- Antithyroid Agents
- Anabolic Steroids
- Antibiotics and Antifungal Drugs
- Birth Control Pills
- Epilepsy Drugs
- Mood Stabilizers
- Weight Loss Drugs
- Vitamin A rich drugs such as Acne Medications
The mechanism of action for each medication is slightly different, but all work by inhibiting different stages of the hair growth cycle. Drug-induced alopecia is usually reversible when a patient stops using the drug but may take up to 12 months for the hair to regrow.
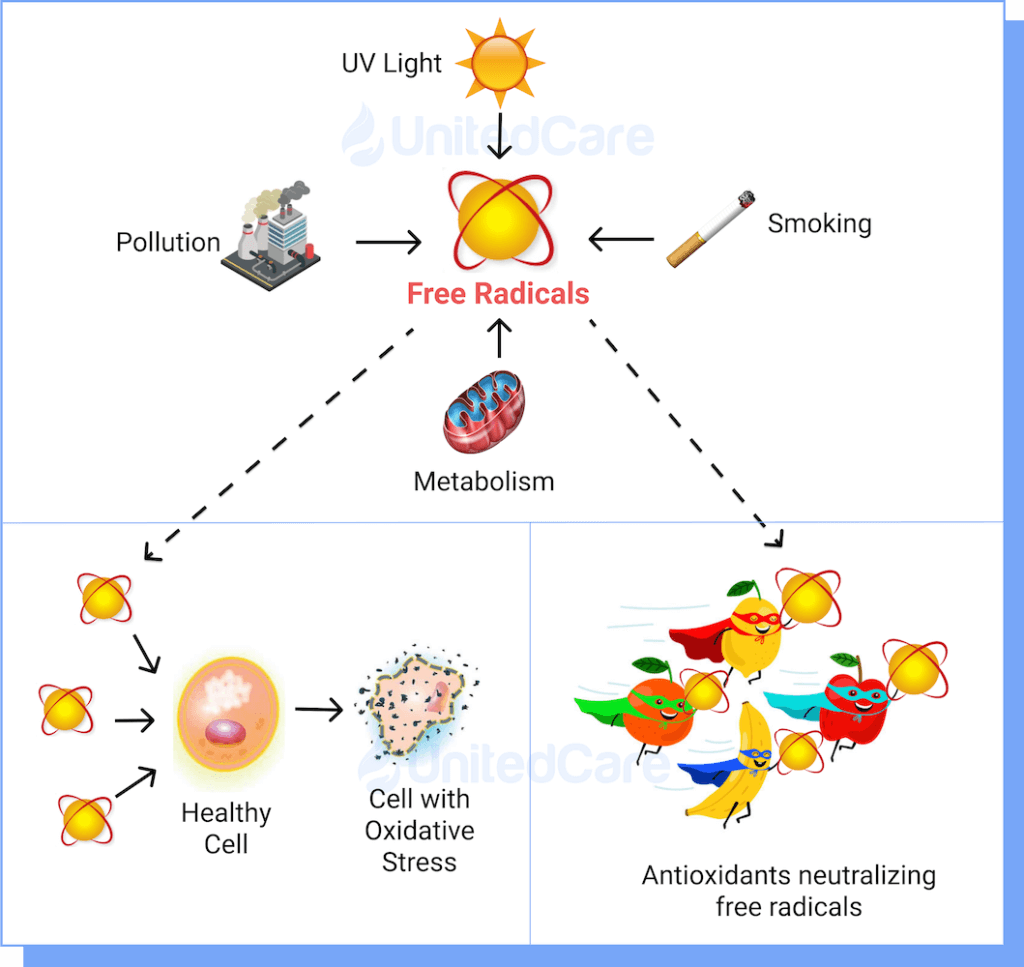
6- Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress is the imbalance between the production of free radicals and antioxidants in your body.
Your body can’t produce enough antioxidants to match free radicals, and the surpass of free radicals damage your cells and DNA.
Oxidative stress can be caused by:
☀ Excessive exposure to sunlight
☁ Pollution
☠ Exposure to chemicals
☢️ Radiation therapy to head
🚬 Smoking
🍺 Alcohol consumption
🍬 Diets high in fat and processed sugar
💊 Certain medications
Oxidative stress will harm your cells and your DNA, accelerating aging and in the scalp, damaging hair follicles that produce hair. Recently, a study focusing on scalp conditions found that oxidative stress plays a huge role in premature hair loss and baldness.
7- Scalp Conditions – oily scalp
Sebum is an oily, waxy substance secreted by our body. It coats, moisturizes, and protects your skin and protects/supports your healthy hair. It is a natural part of our scalp, and thus, everyone’s hair gets oily sometimes.
While paying attention to hair hygiene, we should not forget that normal amounts of sebum/oil are good for scalp health. Some shampoos are pretty strong and might clean up all the healthy sebum.
An oily scalp, often caused by genetics, refers to a condition where an excess amount of oil (sebum) is released in your scalp.
And excess amounts of oils can and will trap and attract dirt, dandruff, and product build-up, which clogs pores and prevents new hair growth.
8- Thyroid Conditions
Thyroid diseases such as hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can cause diffuse hair loss and many other adverse effects on your body if they’re not treated.
The hair thinning and loss is diffuse (no patching or bald spots) is all over the scalp.
Thyroid conditions can disrupt hormone production processes, especially the T3 and T4 thyroid hormones, which help produce hair at the root.
So, a thyroid disease might mean that you’re not getting back the hair you’ve lost.
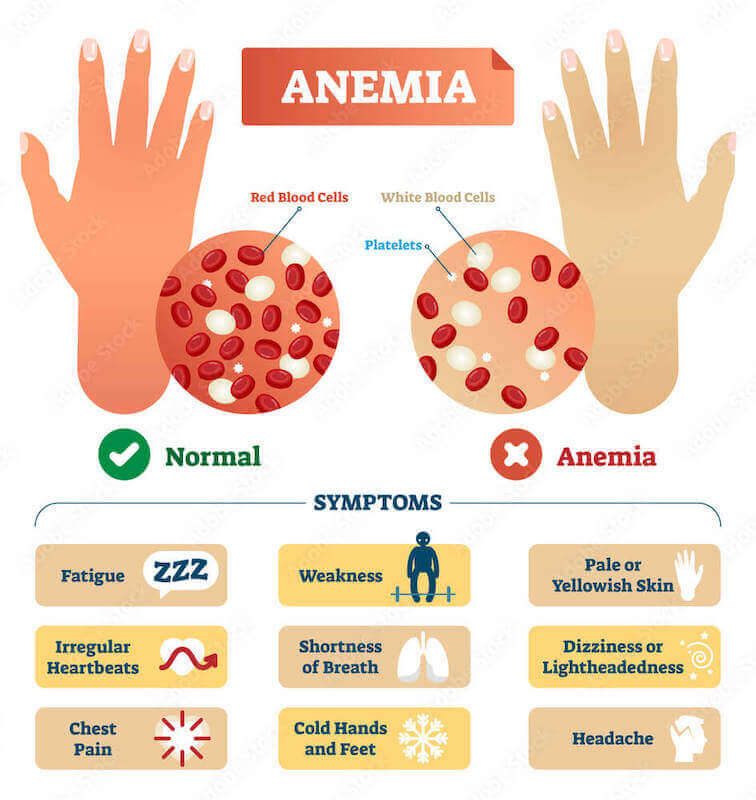
9- Iron Deficiency Anemia
What is Iron Deficiency Anemia?
It is a condition in which the blood doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells. These cells are responsible for carrying oxygen to organs and tissues.
What are Iron Deficiency Anemia Symptoms?
- Extreme weakness
- Pale or yellowish skin
- Fatigue
- Irregular heartbeats
- Headache
- Cold hands and feet
- Brittle nails
- Poor Appetite
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
How does Iron Deficiency Anemia affect hair follicles?
This topic is somewhat controversial.
Some researchers found out it is causing hair loss, and others say there is no clear and proven relation between them.
A study published in the Journal of Korean Medical Science found that Iron Deficiency is an apparent factor in developing or worsening Female Pattern Hair Loss, especially shortly before menopause.
However, in the same study, it is indicated that:
“Iron Deficiency’s role in Male Pattern Hair Loss is hard to conclude.”
Bodies of patients who experience a severe iron deficiency may start cutting oxygen to organs and tissues that are not vital.
Could you guess what needs oxygen? Yes, your hair. So, iron deficiency might cause hair loss by stopping the body from providing your scalp with oxygen.
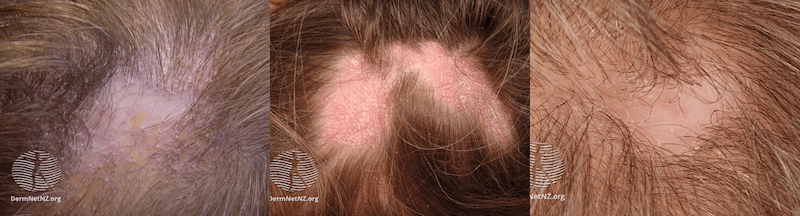
10- Lichen Pilanopilaris
Lichen Planopilaris is an inflammatory condition that causes scarring hair loss. It destroys the hair follicle and then replaces it with scarring, resulting in permanent hair loss (The hair follicles do not regrow).
The cause of this disease is unknown. It is known that the body’s immune system is involved in the process, but the trigger is mysterious.
What are the symptoms of Lichen Pilanopilaris?
Suppose you feel itchiness, tenderness, pain, and burning in your scalp and start to realize areas of hair loss. In that case, you might be experiencing the disease.
Also, your mouth, skin, genitals, nails may show indications.
A dermatologist can detect white dots without hair follicles on your scalp in a trichoscopic examination.
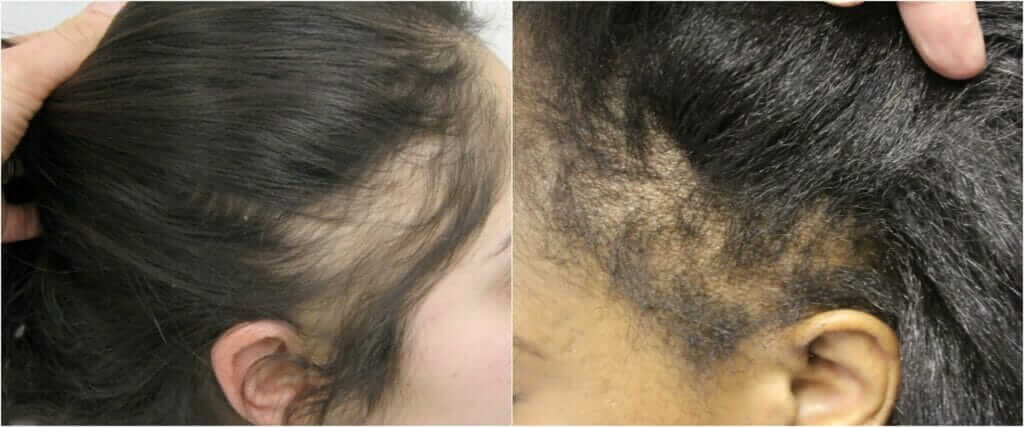
11- Tractional Alopecia
Traction alopecia is hair loss that stems from mechanical damage to hair follicles.
- Repeatedly pulling on your hair,
- Traumatic hairstyling,
- Chemical appliance via styling care or hair coloring products
- Heat appliance via blow dryer or hair straighteners
- Often wearing the hair in a ponytail, bun or braids might cause tractional alopecia.
12- Low Blood Circulation
If you’re not someone who regularly exercises, you’re likely to experience a decrease in blood circulation.
Reduced blood circulation will eventually translate to a decreased scalp blood flow. It will leave your hair without oxygen and nutrition, which can cause hair loss or accelerate your existing condition.
In addition, overly stressed people can experience a decrease in blood flow as well.
In this case, the stress hormone cortisol takes over. It puts your body into a “flight or fight mode,” which diverts blood away from non-essential parts such as the hair follicles for immediate survival.
13- Anxiety and Stress
Although anxiety is not directly related to hair loss, stress caused by anxiety and other influences can cause mainly two different types of hair loss:
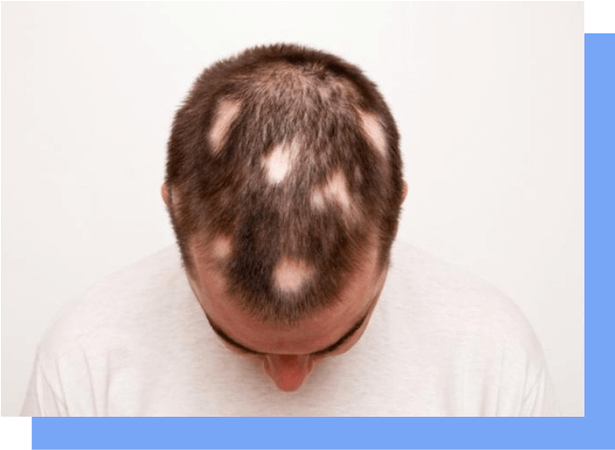
Alopecia Areata:
In this type of hair loss, hair on the head falls out in patches.
Commonly caused by stress, alopecia areata is a condition where the immune system attacks scalp hairs, eventually causing hair loss.
About 6.8 million people are affected by Alopecia Areata in the United States.
The patchy hair loss may be sudden or gradual, and there might be itching or burning in the affected area before hairs start to fall.
The condition may result in total balding if a dermatologist does not treat it.

Telogen effluvium:
In this condition, the hair follicles that produce hair are pushed to a resting phase from their neutral phase, which can eventually result in them falling out of your body.
In an average person, 85% of the hairs actively grow in the anagen phase and 15% in the resting phase.
Suppose there is a traumatic event or stress. In that case, most hair follicles in the anagen phase might change into the resting phase. Eventually, these hair follicles are pushed out by the new hair coming in 2 months after the shock causing sudden hair loss. It is a temporary hair loss, and falling out is a sign of hair regrowth.

14- Lack of Sleep
Sleep connects a person’s time awake with bodily functions such as hair growth and cell division.
In short, we can say that less sleep means less hair follicle growth.
But let’s go a bit more into detail:
In “Sleep Loss Alters Waking Activity in Human Epidermal Keratinocytes,” published in the January 2014 issue of Journal of Investigative Dermatology, researchers studied how cells behave when deprived of restorative rest.
They discovered that with too little sleep, skin cells numbered fewer and formed inappropriately small connections with one another. Both conditions are hallmarks of alopecia areata, the autoimmune disease that causes hair loss.
Sleeping too little also negatively affected the number of melanocytes in the mice studied, which produce pigment for coloring skin and hair.
Although the real effects of lack of sleep on hair loss were recently made clear, you could say the physicians guessed the relation ages ago:
In his book “The Organon of Medicine,” published in six volumes between 1810 and 1820, German physician Samuel Hahnemann reported dozens of case studies involving patients with varying degrees of alopecia treated with homeopathic remedies made from various species of tree moss. Today, many dermatologists recommend that patients receive acupuncture treatment for hair loss. Still, in centuries past, doctors often prescribed hair loss patients with no alternatives for alopecia to sleep on moss-stuffed pillows, which improved sleeping quality back then
15- Nutrition Deficiencies
Lack of specific nutrition will affect different parts of your body and the physical and chemical processes inside. Mainly mineral and vitamin deficiencies correlate with alopecia.
As I’ve mentioned before, Iron Deficiency can be a factor that causes your hair loss. But here are a few other nutritions you should look out for, the most important of them being:
- B12 and Folic acid deficiencies lead to megaloblastic anemia. Too many immature red blood cells cause excessive hair loss, balding, dandruff, and dryness.
- Zinc is essential for insulin production, which is necessary for glucose uptake by muscle cells to produce energy. With a zinc deficiency, you have an increased risk of having dry skin and dandruff. It causes the skin to be more irritated, so it’s susceptible to scalp infections like ringworm.
- Vitamin A is crucial for the cellular growth of hair follicles. However, consumption of too much Vitamin A may lead to Vitamin A toxicity, according to the research. Thus, under and over supplementing can cause hair loss.
- Vitamin E helps the body to protect itself against free radical damage. As we mentioned above, free radicals damage hair cells.
Other than that, nutritional deficiency of
- Niacin,
- Fatty Acids,
- Selenium,
- Vitamin D,
- Biotin,
- Amino acids and Proteins are also known to cause hair loss
The patient should see a dermatologist for a blood test to detect an exact nutritional deficiency causing visible hair loss. If there is no dermatologist, a patient may prefer a family physician or general practitioner as a last resort.
16- Extreme Dietary Habits
Your diet can be a decisive variable in hair loss, as with every health issue.
Overall, balanced and healthy diets will promote hair growth by providing your body with the resources it needs. But if your diet is on the extreme side of the spectrum, you might need to reconsider a few things.
For example, you should steer away from overeating:
1. Egg yolks:
Egg yolks have a high content of sulfur, which is a potent stimulus for the sebaceous glands.
When you overconsume egg yolks, you’ll start producing excess sebum.
And if the amount of sebum increases around your scalp, you’ll end up having an oily scalp that will cause, as we’ve mentioned before, less hair growth.
2. Sugar:
Studies have shown that people suffering from hair loss eat foods with high sugar content more frequently, especially processed sugars.
The loss may be because glucose increases glycoside levels, which can cause toxic effects on cells and interfere with their normal division.
Also, it has been discovered that too much insulin stimulates the process of hair loss. Therefore avoiding consuming too many sugary foods is likely to improve your condition.
3. Pepper:
I hate to be that guy but, you will also need to control your black pepper intake.
Pepper in certain concentrations can cause severe itching and skin irritation, accelerating hair loss and balding. These are due to the piperine chemical substance inside the pepper, which stimulates sebum secretion and gives you an oily scalp.
4. Vitamin A
The body can’t get rid of Vitamin A excess since it is a fat-soluble vitamin.
So consuming high amounts of Vitamin A causes hypervitaminosis A, leading to skin irritation, coarse hair, and partial hair loss.
5. Foods with High Glycemic Index
Again, foods with a high glycemic index will cause your insulin levels to increase, therefore making you more likely to experience hair loss.
17- Rapid Weight Loss
Your body doesn’t like it when you suddenly change its balance.
When you lose a ton of weight out of nowhere, every part of your body will need to adjust how they work, the number of chemicals and hormones and enzymes they produce, and so on.
So any sudden change in your body mass index will bring up high levels of stress in your body. It will then cause telogen effluvium, where the growth of new hair by your hair follicles will be significantly decreased.
18- Protein Powder Intake
Some of the protein powders that contain whey isolates are known to have anabolic steroids. It makes the body produce higher levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and may eventually lead to hair loss.
19- Smoking
Smoking can cause or accelerate hair loss in many ways.
The most obvious way is by affecting your blood circulation. Toxic chemicals in a cigarette will have a high toll on your blood circulation and reduce the amount of blood that flows into your scalp. Reduced circulation leaves hair follicles with less nutrition and oxygen and ends up in hair loss.
And another way it can harm your hair and prevent hair growth is through the pollution it will produce around you. The smoke stays in the environment for a long time and contains toxic substances. These will adversely affect your hair follicles and scalp.
20- Alcohol Consumption
Excessive amounts of alcohol consumption can lead to severe dehydration, not only to your hair and scalp but also throughout your whole body.
This dehydration has a toll on your hair follicles and hair strands and can slow down hair growth while making your hair fall out.
21- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormone disorder related to women’s ovaries. It has three main symptoms, one of which is high androgen levels.
As we’ve mentioned before, high levels of androgen aside from teenage years are never a good sign for your hair.
In most cases, excess androgen will cause noticeable hair loss, showing itself with an overall thinning.
22- Syphilis
Syphilis is an STI (sexually transmitted infection) divided into four stages based on its progression and symptoms.
If untreated, starting from the secondary stage, Syphilis can cause bald patches in your scalp where it affects. However, these bald spots are usually not permanent and recover when treated.
23- Poisoning
Obviously, most chemicals are incredibly harmful to our bodies.
Especially for people that work in labs or chemical substance production lines, exposure to poisonous substances such as mercury, lithium, thallium, and arsenic can result in hair loss.
24- COVID-19 Hair Loss
Hair loss can be observed after a severe illness such as COVID-19. This loss is generally Telogen Effluvium diffuse pattern hair shedding resulting from the early telogen phase entrance.
A recent study reported that ten female patients experienced serious hair loss following laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection. The patients are from different ethnicities with no hereditary hair loss and have a 55 median age.
It is stated that excessive hair shedding began within weeks to months after the COVID-19 infection. Since the patients didn’t report any other medical conditions, they were all diagnosed with Telogen Effluvium.
Stressful events, diseases, drugs, nutritional deficiencies, and sudden weight loss can cause Telogen Effluvium. In TE, more hairs than usual enter the telogen phase simultaneously.
The telogen phase of hair follicles is also called the resting phase, and old hair follicles start to fall to make room for new baby hairs.
An average person loses around 100 hair strands every day (due to the hair growth cycle), which is considered normal.
In general, 84% of scalp hairs are in the anagen, and 16% are in the telogen phase. However, major stress or shock may push up to 50% of hair follicles into the shedding phase.
Furthermore, a Spanish researcher González-Sanguino and colleagues surveyed more than 3000 people. They found that female patients were more likely to be affected by COVID-19 both psychologically and physiologically, showing more significant symptoms of depression and anxiety, and related hair loss. They concluded that women are more likely to seek help for their hair loss condition.
Does the COVID-19 Vaccine Cause Hair Loss?
There is not enough data for us to say that COVID-19 vaccines cause hair loss; research results are not clear.
In one of the studies, the occurrence of Tinea Corporis (ringworm) after vaccination varied from person to person. The reports of hair loss have arrived 2 weeks after the first and 4 months after the second vaccination. However, the result of the study is limited since there is no cause-effect relationship in the cases; there were numerous other factors (such as family history) that were not considered.
In another research in Italy, which is seriously affected by Coronavirus, 3 patients who suffered from Alopecia Areata (Spot Baldness) after the Biontech Covid-19 vaccination were examined. All cases reported that they experienced the disease after the first dose of vaccination.
However, researchers concluded that 3 cases were far less than enough to draw conclusions.
Can You Prevent or Revert Hair Loss?
Stopping hair loss
Once you’ve eliminated all the reasons for hair loss, the amount of hair that’s falling out of your scalp should get back to normal.
You can also try one of the various ways of minimizing hair loss, which you can find out more about in our extensive guide:
Read: 15 Working Methods to Prevent Hair Loss👈
If genetic factors play a significant role in your hair loss and other causes are not present, you may not be able to stop hair loss. However, once your androgenic alopecia (AGA) has settled, there are ways to get back to your natural hairline:
Reverting hair loss
If your hair loss has advanced to a significant and visible level, you might be looking to regrow your lost hair.
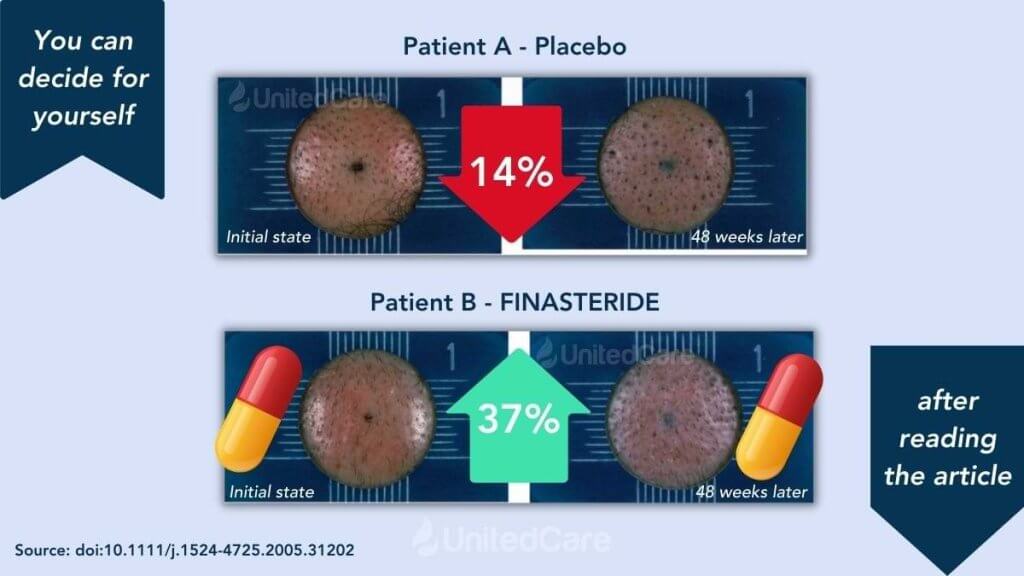
There are numerous non-medical/medical hair loss treatments such as pharmacological medications like Rogaine (Minoxidil) and Finasteride (Propecia), hair massage, herbal therapies, PRP, exercise, and laser therapy. They are backup by studies and can also help hair growth in balding areas.
Also, there are surgical methods such as hair transplantation with FUT or FUE techniques, which is a sure way to get back to your natural look. Our comprehensive guide includes all of these methods:
Next Steps
Yes, we know that detecting the root cause of hair loss is not easy, especially if the underlying medical conditions are unclear.
Each case is unique, and there are a lot of treatments for hair loss (some of them are useless and just marketing). Therefore, only seeing thousands of cases might bring enough experience to diagnose and treat hair loss.
If you need a further diagnosis, assistance, and clinical examination for understanding your hair loss, minimizing it, or getting your natural hairline back, you can always contact hair loss expert dermatologists of UnitedCare or me:
Understanding the reasons behind your hair loss is the first step.
You can learn why and start regrowing your hair with UnitedCare right away:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the cause of hair loss in females?
For women, the most common causes of hair loss are as follows:
- Tractional alopecia (pulling hair too much)
- Anxiety and chronic stress
- Certain medications such as chemotherapy drugs and Vitamin A rich meds
- Age
- Androgen sensitivity
- Extreme dietary habits and rapid weight loss
- Smoking and alcohol consumption
How can I stop my hair loss?
Eliminating the variables that cause your hair loss is the first step to stopping your hair loss. Be aware that there is not a magical solution. You may start with lifestyle changes and Eliminating the variables that cause your hair loss is the first step to stopping your hair loss.
Be aware that there is not a magical solution. You may start with lifestyle changes and dietary updates. You can reduce alcohol consumption and smoking and take supplementary and pharmacological (finasteride, minoxidil) medications. Most importantly, consult with a dermatologist specializing in scalp and hair loss to understand the root cause.
Why am I suddenly losing so much hair?
Multiple reasons can cause sudden hair loss, most common of which are:
- Stress, trauma
- Extreme changes in diet
- Protein powder intake
- Certain medications
- Poisoning from chemical substances
- Male pattern baldness (Androgenetic Alopecia)
What food causes hair loss?
The study proves especially foods high in processed sugars cause hair loss. Other than that, foods that cause insulin increase, such as bread, flour, and sugar with alcohol, endanger hair growth.
What are the types of hair loss?
- Androgenetic Alopecia: It is a medical term of hereditary male or female pattern baldness.
- Telogen Effluvium: It is a noticeable hair loss after an emotional shock and stress. Many hair follicles go into the telogen phase (a.k.a, resting phase) in this condition.
- Anagen Effluvium: It is a hair shedding occurring in hair follicles’ anagen or growth phase due to acute injuries such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy exposure.
- Alopecia Areata: It is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks hair follicles after a stressful event.
- Scarring Alopecias (Cicatricial Alopecia): It is a skin disease in which Inflammation on the skin causes permanent loss of hair. Before a hair replacement surgery, a dermatologist should fix this condition. Otherwise, the operation will fail.
- Alopecia Universalis: In this type of hair loss, all hair son the body (pubic, chest, leg, and scalp) fall out. Hair follicles do not die and can regrow.
- Tinea capitis: It is a ringworm-caused fungal infection resulting in patchy bald spots on the head. Brittle and broken hairs, itchy, red, and ring-like bald spots are some of the symptoms of Tinea Capitis
Can COVID-19 cause hair loss?
Yes, it can. A shock loss may be observed after a serious disease like COVID-19. The cause is generally Telogen Effluvium, in which more hairs than usual go into the resting phase and fall.
What are post COVID-19 hair loss remedies?
If the reason is Telogen Effluvium, hairs tend to get back to normal in 3 to 6 months. Generally, a patient starts to notice baby hairs within two months. If you think your hair loss reason is different from TE (E.g., if you experience patchy losses in contrast to the diffuse pattern loss, which is a characteristic of TE), you need to consult with a dermatologist.
Do women experience more hair loss due to COVID-19?
Generally, women pay more attention to their appearance than men, and they are more sensitive to their looks. Therefore, when experienced with a COVID-19 related hair loss, they exhibit stronger symptoms of depression and anxiety, which trap them in a vicious circle of stress and hair loss.
Do newly transplanted hairs fall out after a successful hair transplant?
Inherently, safe donor zone hairs have fewer ARs (Androgen Receptors). If hairs from the safe zone are used in hair transplantation, they will keep their DHT-resistant property in the newly transplanted area. However, they are still susceptible to DHT even if they are more resistant. Therefore, they may continue falling in years.

Want to learn more about hair loss & hair transplant?
- 💡Your Answer: Hair Transplant vs Finasteride – Surgeon Explains
 You’re having hair loss issues and you’re ready to take action to… Read More »💡Your Answer: Hair Transplant vs Finasteride – Surgeon Explains
You’re having hair loss issues and you’re ready to take action to… Read More »💡Your Answer: Hair Transplant vs Finasteride – Surgeon Explains - PRP vs Finasteride: Is it worth the Cost? Surgeon Explains


 Finasteride vs PRP? Almost every hair loss candidate asks the same question.… Read More »PRP vs Finasteride: Is it worth the Cost? Surgeon Explains
Finasteride vs PRP? Almost every hair loss candidate asks the same question.… Read More »PRP vs Finasteride: Is it worth the Cost? Surgeon Explains - Does PRP Improve Hair Transplant Result? Surgeon Explains

 Everyone who had or is planning to have a hair transplant hears… Read More »Does PRP Improve Hair Transplant Result? Surgeon Explains
Everyone who had or is planning to have a hair transplant hears… Read More »Does PRP Improve Hair Transplant Result? Surgeon Explains

I had COVID in August and into September. After, recovery my hair started falling out. The loss is all over my head. Not patchy. My scalp is very visible before styling. My husband experienced the same thing. His stopped about 3 weeks ago and I’m still loosing hair. I only brush my and style my hair once a day to not add to the stress. I am hypothyroid. Levels were checked in September and were stable. I take vitamins everyday. I have added immune support Bioshield MD in September of this year. I do have a heredity of hair thinning. But, not like this. I’m trying to not freak out. Any help would be great!
Hello Mrs. King,
First of all, I would like to point out that seeing your scalp photos is a must to understand the root cause. Just by reading your story, I can say that your hair loss condition is probably Telogen Effluvium.
There are many sources in the literature stating that many patients complain of hair loss after COVID-19 infection. Although infection and androgen hormones related sheddings are also observed, the most frequent reason is TE.
After COVID-19 infection, a shock loss can be observed since hair follicles switch into the resting/telogen phase and start falling.
I recommend you to get rid of the anxiety and stress via exercises, meditation, yoga, or leisure activities. They only worsen the hair loss condition. Also, there is nothing to worry about if it is Telogen Effluvium. Your hair will grow back in 3 to 6 months.
Don’t hesitate to contact my clinic and get a free hair loss consultation. In this way, I can look at your scalp situation and make a more proper diagnosis.
Hope this answer helps,
Good luck 🍀
Hi my name is Marcy. I’m 67 years old weighing about 213 lbs, 5’ 1”. I live in southwest Washington. I’m a diabetic, have peripheral neuropathy, arthritis. I also suffer from medication, anxiety and stress due to several life issues like family deaths and financial. Though I do not take medication for anxiety. Also I’m always depressed because of weather in Washington state on top of illnesses I have. Weather here is to gray and dark. I feel like I’m suffocating. I’ve been living here for about 4 years.
My hair has suddenly started falling out more than usual. Especially within the last week and a half. What could be causing my hair loss?
Sincerely,
Concerned
Hello Marcy,
I’m very sorry about your condition.
Most probably, peripheral neuropathy and arthritis have developed due to your uncontrolled diabetes. Try to manage diabetes with drugs.
Anxiety and stress worsen overall health and increase cortisol levels. They are common causes of oily skin and hair loss.
As you stated, weather conditions have no direct effect on hair shedding but can affect your mood which indirectly contributes to the loss.
All of these conditions can worsen male-pattern baldness (AGA, the loss is irreversible, I perform hair transplant surgeries to regain the lost hair) and trigger Alopecia Areata (Patchy loss, if treated hair can grow back) or Telogen Effluvium (Severe trauma, illness or stressful event may trigger it, the loss is reversible).
If you send photos of your hair before and after, it will be easier to understand the condition and recommend a treatment course.
And for further diagnosis and help, you may see an endocrinologist and psychiatrist.
Hope this answer helps,
Good luck 🍀